newbie
Rates of interest play a pivotal position in our monetary lives, impacting every thing from our financial savings to the price of borrowing cash. This text goals to delve into two elementary forms of rates of interest: easy and compound. To make knowledgeable monetary choices, it’s vital to know the excellence between them, how they’re calculated, and their potential influence in your funds.
Easy curiosity is an easy idea computed on the unique amount of cash (principal) with out bearing in mind any beforehand collected curiosity. Alternatively, compound curiosity takes under consideration not solely the principal quantity but additionally the curiosity that has accrued over time, resulting in sooner progress. This text will introduce you to their respective formulation, providing a transparent understanding of the right way to calculate compound and easy curiosity. Moreover, I’ll define the important thing distinction between easy and compound curiosity.
My identify is Daria Morgen, and I’ve been within the crypto business since 2014. Having the ability to calculate compound curiosity has been an awesome assist in my very own funding journey, and I hope this text may help you to reinforce your individual buying and selling methods, too.
What Is Easy Curiosity?
Easy curiosity is calculated on the preliminary amount of cash deposited or borrowed. It doesn’t contemplate any curiosity beforehand earned or charged. Many monetary establishments, like banks and credit score unions, use this mannequin for sure merchandise, equivalent to pupil loans and a few forms of financial savings accounts.
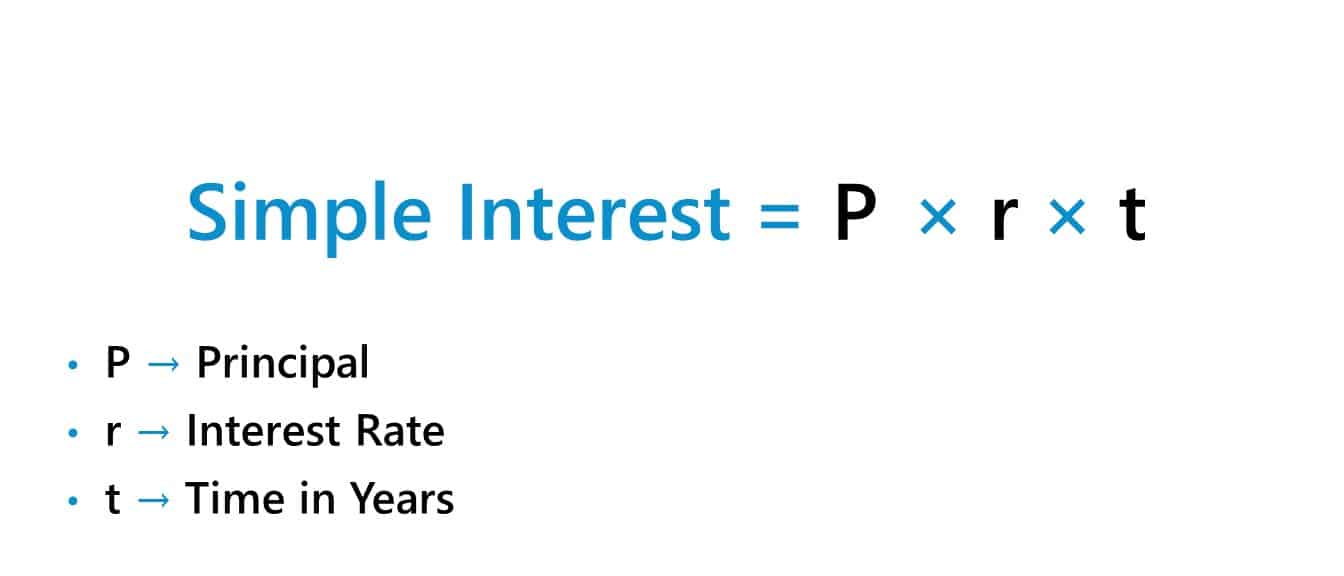
How Does Easy Curiosity Work?
The straightforward curiosity formulation is fairly easy:
Easy Curiosity = Principal * Annual Curiosity Fee * Time
This formulation tells us that the curiosity is a product of the principal quantity, the annual rate of interest, and the time interval for which the cash is borrowed or invested. The time is often expressed in years.
As an illustration, in case you have a bank card that prices easy curiosity, you’re solely ever charged curiosity on the principal stability, no matter any collected curiosity from earlier billing intervals.
Easy Curiosity Instance
Let’s assume you deposit $1,000 in a financial savings account with an annual rate of interest of 5% and depart the cash there for one 12 months. The straightforward curiosity earned could be:
Curiosity = $1,000 * 5% * 1 = $50
On the finish of that 12 months, you’d have $1,050 in your financial savings account.
What Is Compound Curiosity?
Compound curiosity, alternatively, might be regarded as “curiosity on curiosity.” It takes under consideration each the principal stability and the curiosity that has beforehand been added.
Compound curiosity is frequent in lots of monetary merchandise like bank cards, financial savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and even some pupil loans.
How Does Compound Curiosity Work?
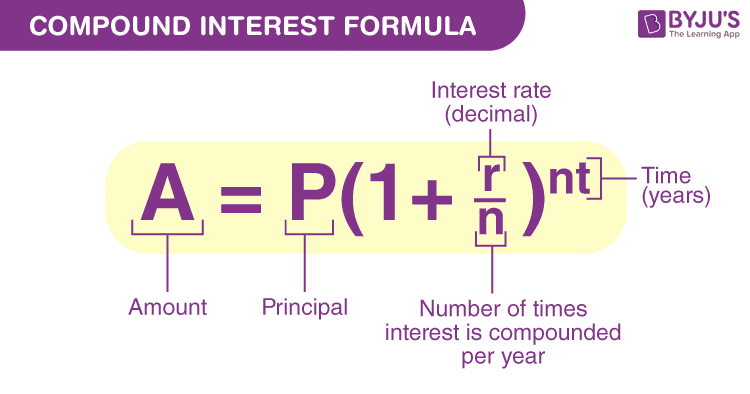
The formulation for compound curiosity is a little more advanced than the straightforward curiosity formulation:
Compound Curiosity = Principal * (1 + Annual Curiosity Fee / Variety of Compounding Intervals)^(Variety of Compounding Intervals * Time) – Principal
This formulation demonstrates that the curiosity is calculated on the preliminary quantity and the collected curiosity from earlier time intervals. The variety of compounding intervals can fluctuate. It may very well be yearly, semi-annually, quarterly, and even day by day.
Compound Curiosity Instance
Let’s take the identical $1,000 deposit at an annual rate of interest of 5%, however this time, the curiosity is compounded yearly. On the finish of 1 12 months, your financial savings account would have:
Curiosity = $1,000 * (1 + 5%/1)^(1*1) – $1,000 = $50
This appears the identical as the straightforward curiosity instance, proper? That’s as a result of the consequences of compound curiosity actually begin to present over longer intervals of time. Let’s say you allow the cash for 5 years as a substitute:
Curiosity = $1,000 * (1 + 5%/1)^(1*5) – $1,000 = $276.28
On the finish of 5 years, you’d have $1,276.28 in your financial savings account. That’s considerably greater than you’d have with easy curiosity.
Easy Curiosity vs. Compound Curiosity. Which One to Select?
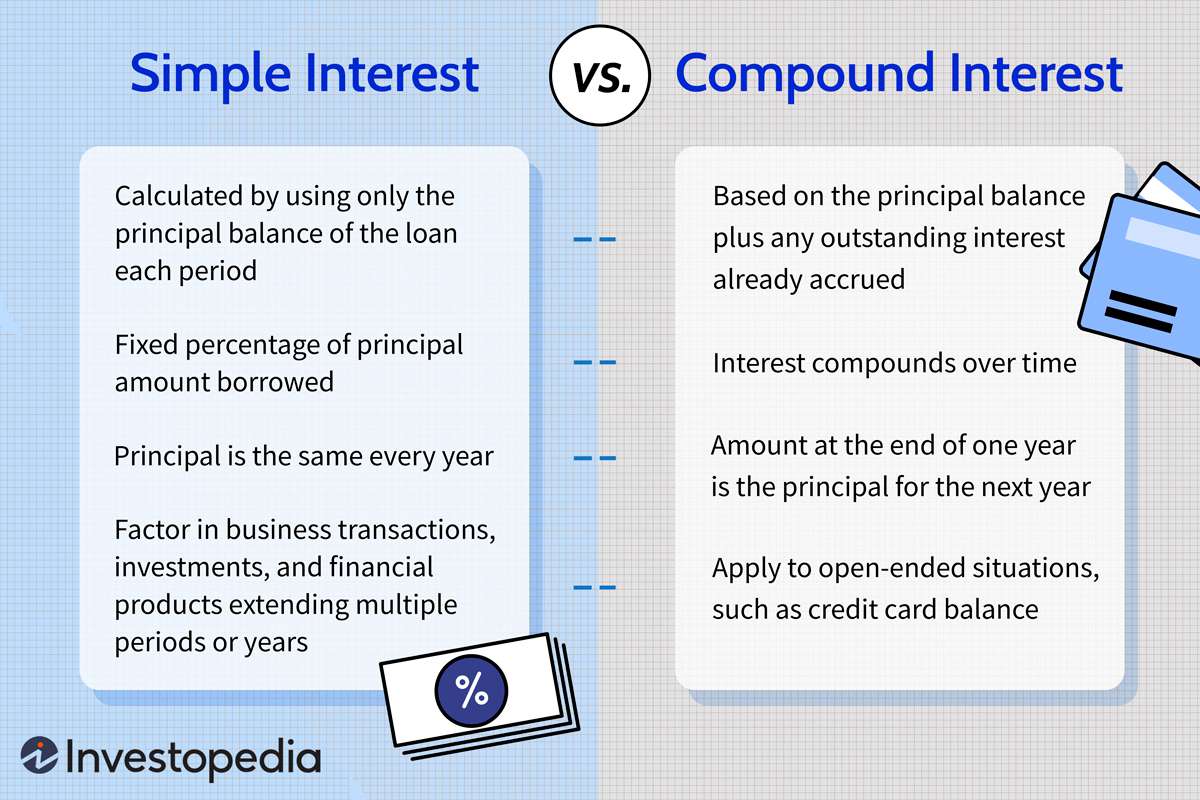
Whether or not easy or compound curiosity is healthier for you depends upon whether or not you’re borrowing or investing cash.
If you wish to borrow cash, you’d typically choose a mortgage with a easy curiosity formulation, as you’d find yourself paying much less over the mortgage time period in comparison with compound curiosity. It is because you’re solely being charged curiosity on the unique principal, not on any collected curiosity.
Conversely, for those who’re investing or saving, compound curiosity may very well be extra useful because it permits your cash to develop at a sooner charge over time because of the impact of compounding. Which means that you earn curiosity not solely in your unique funding but additionally on the curiosity that your funding has already earned.
Easy or Compound Curiosity for Crypto
On the subject of investing in cryptocurrencies, the selection between easy and compound curiosity depends upon your monetary objectives and threat tolerance. If a crypto platform gives curiosity on holdings, compound curiosity might result in extra substantial progress over time. Nonetheless, as with all funding, it’s essential to know the dangers and potential charge of return.
In conclusion, understanding the variations between easy and compound curiosity is vital for making knowledgeable monetary choices. It will possibly vastly influence how a lot you find yourself paying on loans or incomes on investments over a time frame.
FAQ
What’s the formulation for calculating curiosity?
The formulation for calculating easy curiosity is sort of easy: Easy Curiosity = Principal * Annual Curiosity Fee * Time. It’s calculated on the preliminary principal quantity with out contemplating the curiosity that accumulates over time.
In distinction, the compound curiosity formulation is extra advanced: Compound Curiosity = Principal * (1 + Annual Curiosity Fee / Variety of Compounding Intervals)^(Variety of Compounding Intervals * Time) – Principal. Compound curiosity is calculated on the preliminary principal and likewise on the collected curiosity from earlier intervals.
How are easy curiosity and compound curiosity completely different?
The important thing distinction between easy curiosity and compound curiosity lies in how the curiosity accumulates. Easy curiosity is calculated solely on the unique quantity (principal) that you simply deposit or borrow, whereas compound curiosity is calculated on the principal quantity and any accrued curiosity. Which means that with compound curiosity, you earn or owe curiosity on the curiosity.
Which sort of curiosity can earn extra money over the long run?
Over the long run, compound curiosity can earn extra money. That is because of the impact of compounding, the place you earn curiosity on each the cash you’ve initially invested and the curiosity you’ve already earned.
How do easy rates of interest have an effect on month-to-month funds on loans?
For private loans or some other mortgage that makes use of easy curiosity, the month-to-month fee principally stays the identical all through the mortgage time period. It is because the curiosity is calculated solely on the unique principal, and the general mortgage quantity doesn’t enhance because of the extra cash generated by collected curiosity.
Does the frequency of compounding curiosity have an effect on how a lot curiosity you earn or owe?
Sure, the frequency of compounding can considerably influence the quantity of curiosity earned or owed. The extra incessantly curiosity is compounded, the extra curiosity accumulates, offered that the annual charge stays the identical. For instance, curiosity compounded day by day will accrue greater than curiosity compounded yearly.
How does the Annual Share Fee (APR) relate to easy and compound curiosity?
The Annual Share Fee (APR) is a standardized approach of expressing the price of borrowing cash, which incorporates each the rate of interest and any charges related to the mortgage. For loans with easy curiosity, the APR and the rate of interest will sometimes be the identical. Nonetheless, for loans with compound curiosity, the APR shall be larger than the said rate of interest because of the impact of compounding.











![Why Ethereum [ETH] address outflows may be headed for DeFi](https://cryptonoiz.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/AMBCrypto_An_image_of_a_stylized_Ethereum_logo_with_arrows_poin_22f2aeff-c7bb-4c7d-aec7-547a37a35e82-1-1000x600-360x180.jpg)


























